
👤 Rockshell Insights
18/11/2025
When people think of heat pumps, they often picture residential units used for heating and cooling homes. These standard heat pumps are built for comfort, efficiency, and affordability but they’re not designed to withstand the rigors of chemical plants, refineries, or industrial manufacturing floors.
For sectors like chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment, the requirements are completely different. Here, industrial heat pumps particularly chemical-grade systems play a transformative role. They deliver high-temperature performance, corrosion resistance, and process stability in environments where standard systems would fail.
In this blog, we’ll break down the differences between standard vs. industrial heat pumps, highlight the unique features of chemical-grade solutions, and explain why choosing the right type of system is critical for energy efficiency and sustainability.
The Basics: Standard Heat Pumps
Standard or residential/commercial heat pumps are primarily designed for HVAC applications—heating and cooling spaces in homes, offices, and small buildings.
Key Characteristics of Standard Heat Pumps:
- Operating Temperatures: Typically, between –10°C and 60°C.
- Media Handling: Designed for air or water circulation only.
- Construction: Lightweight materials, limited resistance to aggressive chemicals.
- Efficiency Goal: Focus on comfort, indoor air quality, and reducing utility bills.
- Applications: Homes, offices, retail spaces, and small commercial facilities.
While highly efficient for their intended purpose, standard heat pumps are unsuitable for demanding industrial processes that require continuous, high-grade heat.
Industrial Heat Pumps: Built for the Toughest Jobs
Industrial heat pumps are designed to operate at higher capacities and temperatures while handling aggressive fluids and extreme conditions.
Key Characteristics of Industrial Heat Pumps:
- Operating Temperatures: Can exceed 100–160°C, depending on the system.
- Durability: Built with stainless steel, titanium, or special alloys to resist corrosion.
- Efficiency: Achieve high COP (Coefficient of Performance) values, ensuring lower energy use compared to boilers.
- Customization: Engineered for process-specific applications such as drying, evaporation, distillation, or hot water generation.
- Applications: Chemical plants, pharma industries, food processing, wastewater treatment, and more.
Industrial heat pumps don’t just provide heating and cooling—they integrate into the process chain, recovering waste heat and delivering consistent, reliable energy.
Why Chemical-Grade Heat Pumps Are Different
Among industrial systems, chemical-grade heat pumps are a class of their own. They are purpose-built for handling alkaline solutions, acidic chemicals, corrosive fluids, and high-temperature processes.
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials
Chemical processes often involve aggressive substances like acids or alkalis that can corrode standard equipment quickly. Chemical-grade heat pumps use:
- Titanium heat exchangers for durability.
- Stainless steel 316/duplex alloys for resistance to corrosion.
- Special coatings to prevent material degradation.
This ensures longer lifespan and fewer breakdowns compared to standard or even generic industrial units.
- Higher Temperature Capabilities
Chemical reactions often require temperatures above 100°C. Chemical-grade heat pumps are engineered to deliver consistent, precise heating at elevated ranges—something standard heat pumps simply cannot achieve.
- Energy Efficiency with High COP
While boilers burn fossil fuels with ~80–90% efficiency, chemical-grade heat pumps can reach COPs of 3–6, even at high temperatures. This translates into 40–60% energy savings for industries that run heating systems 24/7.
- Custom Design for Process Integration
Unlike off-the-shelf HVAC units, chemical-grade heat pumps are custom-engineered to integrate seamlessly with:
- Vacuum evaporators
- Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems
- Distillation columns
- Drying systems
This makes them integral to the production line, not just an add-on.
- Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Chemical industries face strict regulations on energy use, emissions, and wastewater. By reducing fossil fuel dependency and enabling waste heat recovery, chemical-grade heat pumps help businesses:
- Meet ESG and CSR goals.
- Stay compliant with global sustainability norms.
- Reduce CO₂ emissions significantly.
Standard vs. Industrial Heat Pumps: A Comparison
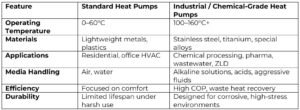
This table makes it clear: chemical-grade systems are engineered for survival and efficiency where standard units fail.
Example: Evaporation in Chemical Processing
A chemical manufacturer using standard heating methods (boilers) for evaporation was spending a large portion of operational costs on fuel consumption. Switching to industrial high-temperature heat pumps allowed the plant to:
- Reuse latent heat of vaporization.
- Cut energy consumption by 50%.
- Reduce annual CO₂ emissions by over 1,500 tonnes.
- Increase process stability and product quality.
This example highlights why the right heat pump choice makes all the difference.
The Business Case for Chemical-Grade Heat Pumps
For decision-makers in the chemical industry, the advantages go beyond technical performance:
- Lower OPEX: Significant energy and maintenance savings.
- Faster ROI: Typical payback periods of 2–4 years.
- Competitive Edge: Lower costs and greener processes appeal to clients and investors.
- Future Readiness: Prepared for stricter emission and energy regulations.
Rockshell Corp: Pioneering Industrial Heat Pump Solutions
At Rockshell Corp, we specialise in designing and manufacturing industrial and chemical-grade heat pumps tailored to the needs of chemical plants and industrial clients.
Our systems are:
- Built with corrosion-resistant alloys.
- Designed for high COP and reliable performance.
- Integrated with applications like ZLD, evaporators, and chillers.
- Manufactured in India, following global engineering standards.
👉 Learn more about our Heat Pump Solutions
Future Outlook: The Rise of Industrial Heat Pumps
As global industries move towards carbon neutrality, the adoption of chemical-grade heat pumps will accelerate. With governments pushing for renewable integration, net-zero targets, and energy efficiency, chemical industries must invest in next-generation heating technologies to remain competitive.
The future is clear: industrial heat pumps will not just complement boilers – they will replace them.
Conclusion
Standard heat pumps are excellent for residential comfort, but they simply can’t survive the harsh demands of chemical processing. Industrial, chemical-grade heat pumps provide the durability, efficiency, and performance needed to handle corrosive fluids, high temperatures, and 24/7 operations.
By investing in these advanced systems, chemical manufacturers can achieve:
- Massive energy savings
- Lower carbon footprints
- Regulatory compliance
- A sustainable future
For companies in India and beyond, choosing a reliable industrial heat pump partner like Rockshell Corp ensures long-term success and resilience in a rapidly changing energy landscape.

